News
What is GPON?
2024-01-30
GPON (Gigabit-Capable PON) technology is the latest generation of broadband passive optical integrated access standard based on ITU-TG.984.x standard, with high bandwidth, high efficiency, large coverage, rich user interfaces, and many other advantages, is considered by most operators as the ideal technology to achieve broadband access network services, integrated transformation. The maximum downlink rate of GPON is 2.5Gbps, the uplink rate is 1.25Gbps, and the maximum split ratio is 1:64.
GPON Standard
GPON was firstly proposed by FSAN in September 2002, and ITU-T completed the formulation of ITU-T G.984.1 and G.984.2 in March 2003, and the standardisation of G.984.3 in February and June 2004 on this basis. Thus, the GPON standard family was finally formed.
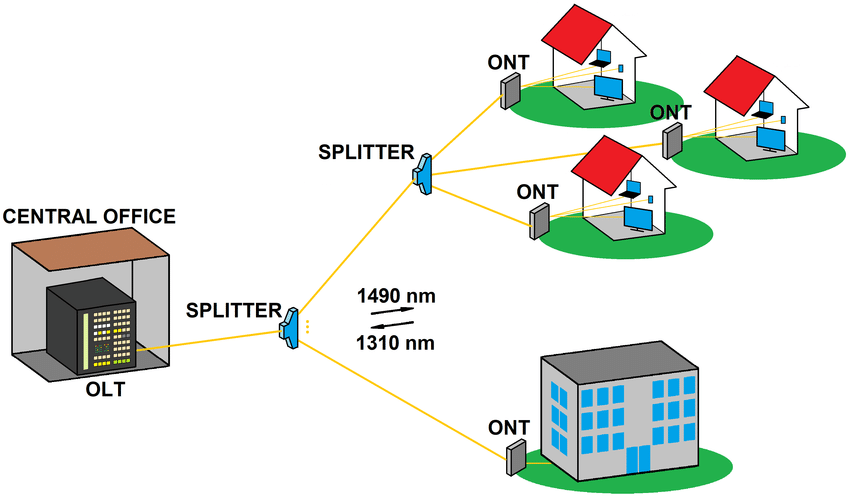
The basic structure of the equipment based on GPON technology is similar to that of the existing PON, which also consists of OLT (Optical Line Terminal) at the bureau end, ONT/ONU (Optical Network Terminal or Optical Network Unit) at the user end, and ODN (Optical Distribution Network) consisting of single-mode optical fibre (SM fibre) and passive splitters (Splitters) connecting the first two types of equipment as well as the network management system.
For other PON standards, the GPON standard provides unprecedented high bandwidth, downlink rate of up to 2.5Gbit/s, its asymmetric characteristics more adaptable to the broadband data service market.
Provides full-service guarantee of QoS. Carrying both ATM elements and/or GEM frames, it has the ability to provide good service level, support QoS guarantee and full-service access. When carrying GEM frames, TDM services can be mapped into GEM frames, and TDM services can be directly supported using standard 8kHz (125μs) frames. As a carrier-grade technology standard, GPON also specifies protection mechanisms and full OAM functionality at the access network level.
The GPON standard specifies the types of services that need to be supported, including data services (Ethernet services, including IP services and MPEG video streaming), PSTN services (POTS, ISDN services), private lines (T1, E1, DS3, E3 and ATM services) and video services (digital video). The multiple services in GPON are mapped into ATM elements or GEM frames for transmission, providing appropriate QoS guarantees for each service type.
GPON Networking Methods
At present, GPON mainly adopts three kinds of networking methods:
FTTH/O, FTTB+LAN and FTTB+DSL
FTTH/O is fibre-to-the-home/office. The optical fibre is directly connected to the user's ONU after entering the splitter, and an ONU is only used by one user, with high bandwidth and high cost, which is generally targeted at high-end users and commercial users.
FTTB+LAN is fibre to the building, and then through the high-capacity ONU (called MDU) to access different services to multiple users, so multiple users share the bandwidth resources of an ONU, each occupying a lower bandwidth, and the cost is also low, generally for low-end residential and low-end commercial users.
FTTB+ADSL is fibre to the building, and then the service will be accessed to multiple users in the way of ADSL, also multiple users share one ONU, and the bandwidth, cost and customer base are similar to FTTB+LAN.